| ETHYLENEGLYCOL MONOBUTYL ETHER ACETATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 112-07-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 203-933-3 | |
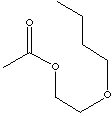
| FORMULA | CH3COOCH2CH2O(CH2)3CH3 | |
| MOL WT. | 160.212 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2915.39 | |
| TOXICITY | Oral rat LD50: 2400 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | 1-Acetoxy-2-butoxyethane; Ethanol, 2-butoxy-, acetate; | |
| Butylcellosolve acetate; Ethylene glycol mono-n-butyl ether acetate; Butylglycol acetate; Acetic acid, 2-butoxyethyl ester; 2-Butoxyethanol acetate; 2-Butoxyethylester kyseliny octove; Butylcelosolvacetat; Ektasolve eb acetate; Glycol monobutyl ether acetate; Butoxyethyl acetate; Ethylene glycol butyl ether acetate; Butoxyethanol acetate; n-Butyl cellosolve acetate; 2-Butoxyethyl acetate; | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | -63 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 192 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.94 - 0.945 |
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Miscible | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
645 C | |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1 Flammability: 2 Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | 76 C | |
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions |
|
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Glycol ethers, with the combination of ether, alcohol and hydrocarbon chain in one molecule, provide versatile solvency characteristics with both polar and non-polar properties. The chemical structure of long hydrocarbon chain resist to solubility in water, while ether or alcohol groups introduce the promoted hydrophilic solubility performance. This surfactant-like structure provides the compatibility between water and a number of organic solvents, and the ability to couple unlike phases. Glycol ethers are characterized by their wide range of hydrophilic/hydrophobic balances. glycol ethers are used as diluents and levelling agents in the manufacture of paints and baking finishes. Glycol ether series are used in the manufacture of nitrocellulose and combination lacquers. They are used as an additive in brake fluid. They are formulated for dying textiles and leathers and for insecticides and herbicides. They provides performance in cleaners products with oil-water dispersions. They are used in printing industries as they have a slow evaporation rate. They are used as a fixative for perfumes, germicides, bactericides, insect repellents and antiseptic. They are used as an additive for jet fuel to prevent ice buildup. Glymes, dimethyl ethers, have two terminal methyl groups which offer stability and high solvency. They are useful as solubilizers and phase transfer catalysts. Glymes offer the property required as an inert reaction medium chemical reaction due to their low chemical reactivity. They are suitable particularly for organometallic and polymerization reactions. Glycol ethers which contain hydroxyl group are also useful chemical intermediate. The hydroxyl group will undergo reaction with aldehydes (or ketones) to produce hemiacetals (or acetals), with epoxides to produce polyether alcohols, with halogenating agents to produce alkoxy alkyl halides, with carboxylic acid compounds or inorganic acids to produce a number of esters. Acetate is the ester that an organic group replaces a hydrogen atom in -OH group of acetic acid through reaction (typically condensation) with alcohols. Condensation is the reaction in which two molecules having -OH groups are joined with eliminating a water molecule from their -OH groups. They are produced by esterification reaction from acetic acid and the corresponding alcohol in the presence of strong acids like sulfuric acid. This reaction is reversible and acetate can be hydrolyzed back into alcohol and acetic acid in the presence of strong bases or strong acid, especially at elevated temperature. The term acetate is also for the salt that one or more of the hydrogen atoms of acetic acid are replaced by one or more cations of the base, resulting in a compound containing the negative organic ion of CH3COO-. Lower acetate is a non-polar to weak polar aprotic solvent which have some solubility portion in water. Its miscibility with water gets higher at elevated temperature. Higher acetates have a low solubility in water and used as extraction solvents for fine chemicals particularly for certain antibiotics. Organic acetates are good solvents for a broad range of resins as they are miscible with almost all common organic liquids. Due to their powerful solvency, high volatility and mild odor, acetates are widely used as solvents for paints, coatings, adhesives, cellulose, plastics, fats, wood stains. Additionally ether acetates series are also widely used as solvents. This surfactant-like structure provides the compatibility between water and a number of organic solvents, and the ability to couple unlike phases. The main products include ethyleneglycol monoethyl ether acetate, ethyleneglycol monobutyl ether acetate, and propyleneglycol monomethyl ether acetate. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid | |
|
PURITY |
99.0% min |
|
|
COLOR, APHA |
15 max |
|
| ETHYLENE GLYCOL |
0.3% max |
|
|
WATER |
0.15 max |
|
|
TRANSPORTATION |
||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. |
|
|
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 20/21, Safety Phrases: 24 | ||